Introduction
We provide a few examples, to illustrate the syntax of SNB.
These examples might also be used to understand the GML formalism for the SNB, and are also base tests for the exportToGML plugin.
All these examples are provided in CAMI format, so that they can easily be imported into Coloane.
To import those models into Coloane, first create a Modeling Project.
Right click on this project, choose Import..., then Cami File under the Coloane submenu.
Choose the file you want to import (e.g. 'vote_SN.cami'), and the formalism 'Colored Petri Net'.
To export a model you have imported or created with Coloane to GML format, right-click on it, and choose Export....
Select GML under the Coloane submenu.
You then have to select the models you want to export (you can export different models at a time), and a destination folder.
The voters (Symmetric Net version)
This is a simple example : several voters are initially in the INIT place.
Two transitions, called YES and NO, make them vote, one at a time, either "yes" or "no".
This net is very simple to understand, and recalls the basic syntax for SN.
It also shows how to define colour symmetries.
In the declarative part, the line following the keyword "EQUIVALENCES" means that we distinguish two groups of voters : the first group includes voters from 1 to 5, and the second one includes voters from 6 to 10.
Inside each group, all the voters are equivalent, but two voters in different groups are not.
In this case, our model corresponds to the analysis of a vote with respect to two populations of voters.
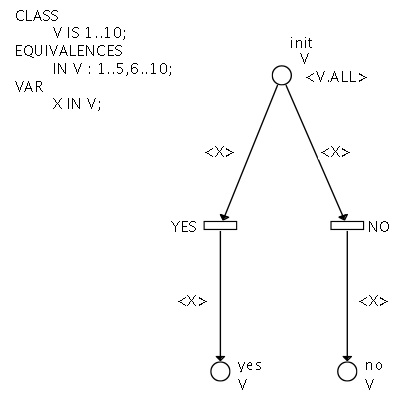
Figure 1 : the Voters (SN version)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Voters (SN)
The voters (Symmetric Net with bags version)
This is a rewriting of the voters model presented in the previous section.
The variable 'X' is bound to a multi-set of voters, with the condition (the guard of the unique transition) that each voter appears at most once in X.
Shortly, the variable 'X' is actually bound to a set of voters.
When the transition is fired, all voters are removed from the INIT place, all the voters appearing in 'X' vote 'yes', the other ones vote 'no'.
'<~X>' means 'the complementary of X' : <~X> = <V.ALL> - X.
Compared to the SN version, the voters all vote at the same time.
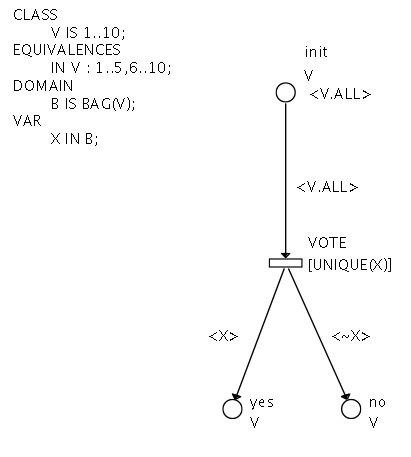
Figure 2 : the Voters (SNB version)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Voters (SNB)
The Client/server (Symmetric Net)
We model here a simple client-server protocol.
A client emits a request for a server, and waits for the response.
When a server is available, it treats one request it has received (one request at a time).
Then it sends a response to the client, that becomes active again, and can emit other requests.
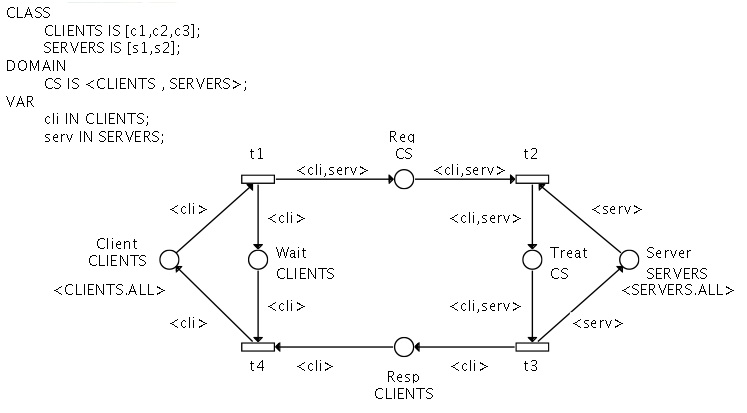
Figure 3 : the Client/Serveur (SN)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Client/server (SN)
The Client/server (Symmetric Net with Bags)
This is a rewriting of the previous one using some SNB features.
The main difference is the behavior of clients : several clients may request the same server at the same time (transition t1).
But the servers always treat the requests one by one.
The responses to clients may also be sent simultaneously, so that several clients may be released at the same time (transition t4).
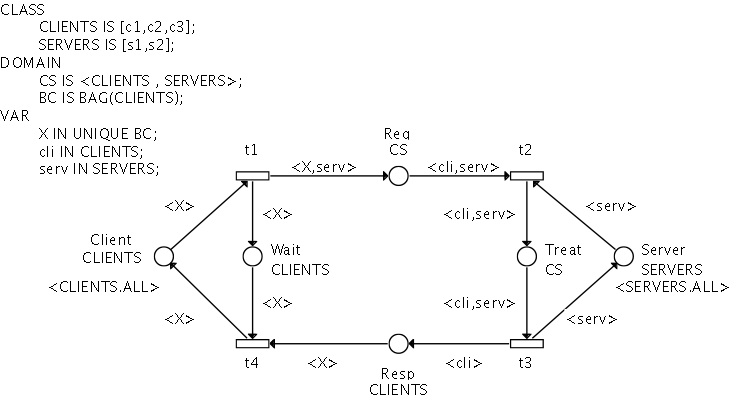
Figure 4 : the Client/server (SNB)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Client/server (SNB)
Shared Memory (Symmetric Net)
This last example models processes sharing memory.
Each process has a reserved part of memory, but may use the memory of other processes.
The model mainly illustrates the affectation of memory segments to processes, ensuring that two processes do not use the same segment at the same time.
Besides, only one process can access another process' part of memory at a time.
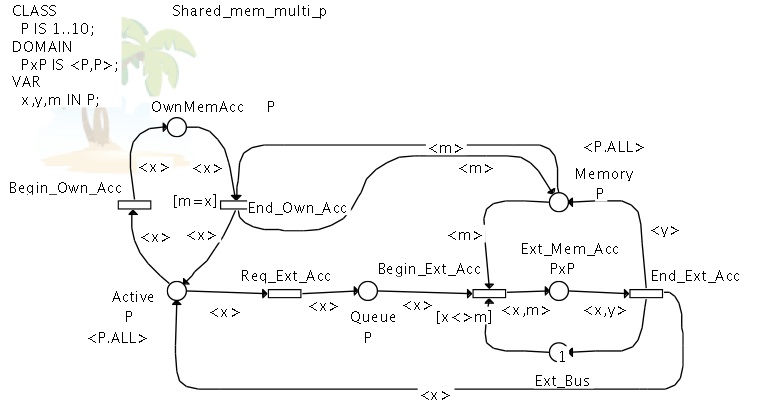
Figure 5 : the shared memory (SN)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Shared memory (SN)
Shared Memory (Symmetric Net with Bags)
Once again, this model is a SNB version of the previous one.
Several processes may access their respective own memory segments at the same time.
The behavior of the access to extern memory segment is not modified.
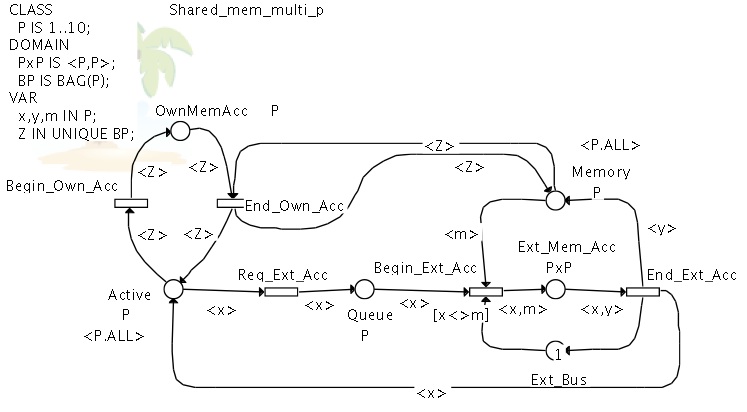
Figure 6 : the shared memory (SNB)
Get the model (importable CAMI format): Shared memory (SNB)
|







